When Must You Change Single-Use Gloves?
Disposable gloves have skyrocketed in use by the general population these past few years, obviously due to the spread of …
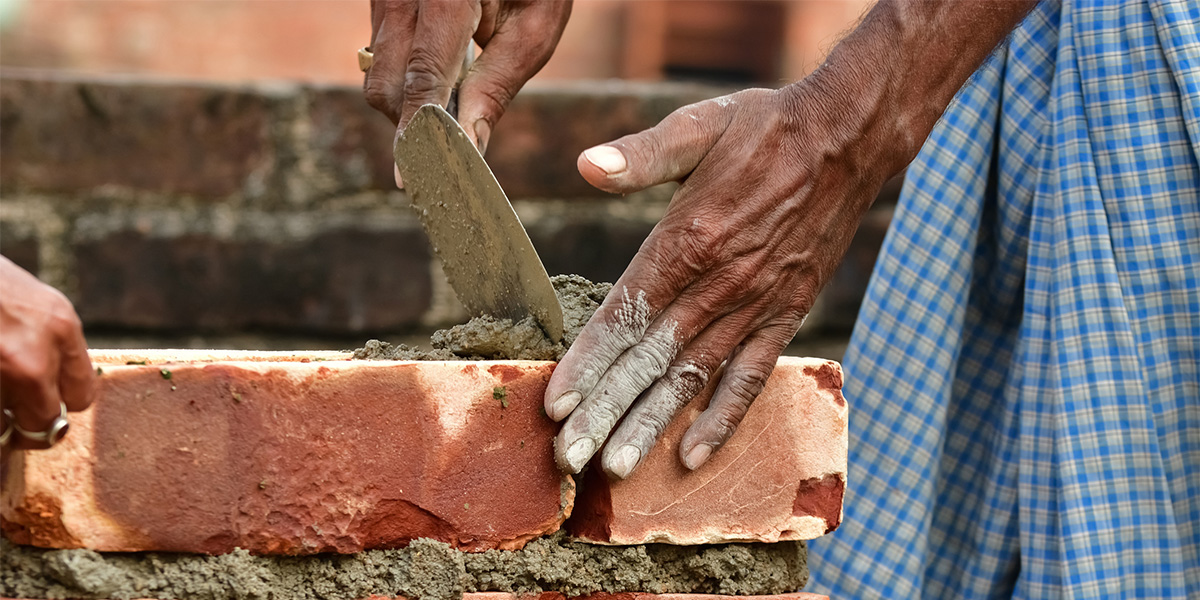

For construction workers and DIY enthusiasts alike, cement burns are a serious but often overlooked hazard.
With the U.S. producing around 84 million tons of cement in 2024 alone, cement can be found all around us. From buildings and bridges to roads and sidewalks, cement is an integral part of our world's infrastructure, and we all rely on it heavily, whether we notice it or not.
However, the chemical composition of wet cement makes it unsafe for contact with skin and can cause serious burns and injuries. For those who handle it, cement is more than a commodity — it is a material that requires safe and proper protocols.
This guide explores what cement burns are, how to treat them, and how you can prevent them with the use of protective work gloves and safe working practices.
Cement burns are chemical or exothermic burns on the skin caused by contact with wet cement.
In general, the more prolonged your contact with the cement is, the more severe your cement burn will be.
Symptoms of cement burns vary depending on the severity of the burns:
Due to the variety of chemicals in cement and its rough texture, there are multiple ways in which cement can cause burns on your hands and skin.
Cement burns are primarily caused by the high alkaline content of wet cement and can manifest as both heat burns and chemical burns.
Wet cement contains calcium hydroxide — otherwise known as slaked lime, caustic lime or hydrated lime — which has a very high pH level of between 12 and 13.
When the alkaline cement makes contact with your skin, it reacts with the water and sweat on the surface of your skin. This powerful reaction breaks down your skin's collagen fibers, fats and proteins, damaging the skin.
Many of the materials present in cement cause it to have a rough and abrasive texture.
Clinker, the main ingredient of cement, exists in small, nodular pieces that can cause abrasions on the skin when direct contact occurs. Cement also contains dry powder, which can have a similar effect on the skin.
Although the texture itself may not cause cement burns, the abrasion can create small cuts on the skin, which enable the alkaline reaction to penetrate more deeply and cause more severe burns.
Some types of cement contain chemicals that are highly toxic to your skin.
For example, many kinds of Portland cement naturally contain hexavalent chromium, which is a carcinogen known to cause chemical burns, skin irritation and contact dermatitis.
Commonly considered an occupational hazard, cement burns are primarily a risk to those who handle the material as part of their job.
Anyone who handles cement is at risk of experiencing cement burns, including:
In particular, those who pour and mix wet cement are most likely to get cement burns.
When handling cement, you are at risk of experiencing cement burns on your hands.
If you or someone you know experiences cement burns, it is important to follow health and safety protocols immediately to minimize damage and avoid long-term health effects.
Depending on the severity of the burns, there are different protocols you should follow.
If you have brief contact with wet cement and experience mild cement burns on your hands, follow these first-aid steps:
If you experience more serious cement burns, seek immediate medical attention.
Seeking immediate medical attention is particularly important if:
Depending on the nature of the burn, a healthcare professional may rinse and dress the area, provide antibiotics to avoid infection, or, for more severe burns, remove damaged skin and perform a skin graft.
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), one of the most effective ways to prevent cement burns on your hands is to wear high-quality protective work gloves.
In particular, protective cement gloves that contain nitrile foam effectively resist chemicals and abrasion, helping minimize your risk of obtaining chemical or heat burns from cement.
As well as wearing industrial-grade personal protective equipment (PPE), you can prevent cement burns on your hands by following these safety protocols:
We have over 20 years of experience providing reliable safety solutions to a variety of industries, so when you wear Glove America protective products, your hands are in safe hands.
At Glove America, we pride ourselves on providing gloves that effectively protect against irritants without compromising your dexterity or control over hand movements.
To find out more about our array of protective work gloves, check out our work glove guide, contact our experts online, or call us at 1-800-476-9657.
Linked Sources:
We’re Here to Help
Give our representatives a call or contact us online today. We’ll be happy to assist you!
Most orders ship same day they are placed. Delivery to contiguous U.S and Canada 1-4 business days.